Tectonic Plates: What They Are, What They Are, Movement, Limits
Have you heard of tectonic plates? These large, complex pieces of the geological puzzle are responsible for shaping our planet as we know it today. The movement of these plates can cause earthquakes, volcanoes and even the formation of mountains. If you want to better understand how they work and how they influence the world around us, this is the right place to start.
Earth is a rocky ball with a hot core, a thick mantle and a thin outer crust. And it is in this crust that we find the tectonic plates that move slowly over the surface of the planet. They are in constant motion, and that motion may be responsible for many of the geological events we see in our world. This movement is one of the most powerful forces shaping our planet.
These plates can move in different directions and speeds, and their edges can be converging, diverging, or transforming. And this and much more information you find in the following article.
What are Tectonic Plates?
Tectonic plates are large blocks of Earth’s crust that move slowly over the Earth’s mantle. They are composed of rocks and cover the surface of the planet like a giant jigsaw puzzle. The theory of plate tectonics suggests that the Earth’s crust is divided into many giant pieces that move due to convection currents in the Earth’s mantle.
The movement of these plates can cause earthquakes, volcanoes and the formation of mountains over geological time. The study of plate tectonics is critical to understanding Earth’s geology and how our planet has changed and evolved over the years.
Read too:
– Apps to detect earthquakes: Real-time emergency alerts
– Richter Scale: How it came about, What is it for, Calculation, Maximum Value
What are Tectonic Plates?
There are seven major tectonic plates and several smaller ones that move slowly in different directions and eventually collide or pull apart. Their theory was first proposed in the 1960s by a group of scientists after the observation that the earth’s crust was divided into several plates that moved in different directions. Since then, several studies and research have been carried out to better understand how these plates move and what the consequences of this movement are.
In short, tectonic plates are rocky blocks that make up the Earth’s crust and are in constant motion, which can cause natural phenomena. It is important to study these motions to better understand the Earth and prepare for possible natural disasters.
What are the effects of moving tectonic plates?
The movement of tectonic plates is responsible for several consequences that directly affect the surface of the Earth. This movement can cause:
- Earthquakes;
- Volcanic eruptions;
- Mountain formation;
- Opening of valleys;
- Creation of oceans and continents.
Earthquakes
Earthquakes are common consequences of the movement of tectonic plates. When they move, they can bump or slide against each other, creating pressure and tension in the rocks. When this tension is suddenly released, an earthquake occurs.
Depending on the intensity of the earthquake, it can cause severe damage to cities and people living in the affected areas.
Volcanic eruptions
These may also be consequences of the movement of tectonic plates. When two collide, one can be pushed under the other and come into contact with the hot magma in the Earth’s mantle. This can cause a volcanic eruption, which can release ash, lava and toxic gases into the atmosphere, affecting the climate and environment.
mountain formation
Also, the movement of tectonic plates can result in the formation of mountains. When two collide, one of them can be pushed upwards, forming a mountain range. This process is known as orogeny and can take millions of years to occur.
Opening of vouchers
Plate movement can also result in the opening of valleys and the creation of oceans and continents. When they move away from each other, this can create an opening area in the middle of the ocean, allowing seawater to fill in the empty space and creating a new ocean. Also, when two plates collide, one of them can be under the other, resulting in the formation of a continent.
In summary, the consequences of moving tectonic plates can be extremely impactful for Earth and for human life.
What are the types of Tectonic Plates?
There are seven major tectonic plates and several smaller ones that make up the Earth’s crust. The main seven are:
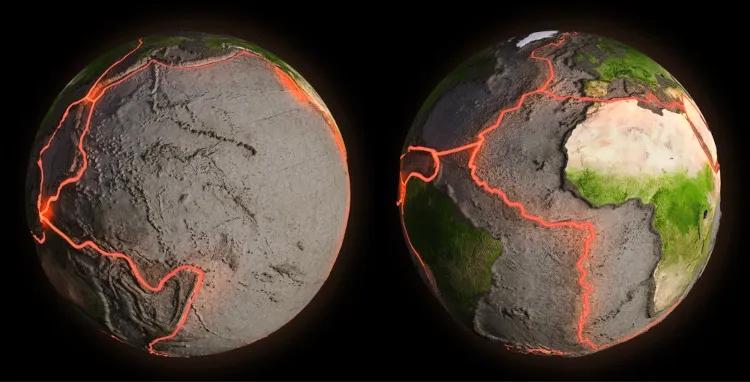
- North American Plate;
- South American Plate;
- African plate;
- Euro-Asia Plate;
- Indo-Australian Plate;
- Antarctic Plate;
- Pacific Plate.
They are always moving slowly in different directions and they collide or move away from each other. The boundaries between plates are called margins, and there are three main types of margins: convergent, divergent, and transform.
What are the boundaries of tectonic plates?
As we have seen, tectonic plate boundaries are the points where plates meet and interact. There are three main types of limits:
- Convergent: two plates collide and one ends up being subducted (dives) under the other. This can cause earthquakes, volcanoes and mountain formation.
- Divergent: plates move away from each other and this can result in the opening of valleys and the creation of oceans.
- Transformants: Plates move laterally relative to each other, causing earthquakes.
In addition to the three main types of boundaries, there are also other types of interactions between plates, such as:
- Oblique slip boundaries: where plates move laterally relative to each other, but without creating or destroying Earth’s crust.
- Hot plate boundaries: Plates are heated by the magma beneath them, which can result in volcanoes.



Deixe um comentário